Best Way to Explain What Is the Difference Between Coin and Token Crypto full Guide.
Coin and Token, Coins are cryptocurrencies that are part of a blockchain. They are independent of other chains and, in their native form, cannot be employed on other chains. Coin applications include:
Money as a medium of exchange
Value storage
monetary unit
Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Dogecoin are among the most prominent coins.
A coin is created by mining, which means that computers solve challenging arithmetic puzzles and validate transactions to create coins. The first computer to answer the puzzle wins newly minted coins. This ensures the system’s security and decentralization.

Coins have the following features and benefits:
Decentralization refers to the fact that coins are not controlled by any central authority or intermediary. They are regulated by their protocol’s rules and the consensus of their community. This provides users with greater control and privacy over their transactions and funds.
Cryptography and encryption are used to protect coins. They are impervious to hacking, censorship, and fraud. Users may be confident that their coins are secure and genuine without relying on third parties.
Scarcity: Most coins have a finite supply determined by their algorithm. This has a deflationary impact, increasing the currency’s value over time. Bitcoin, for example, has a total supply of 21 million, whereas Ethereum is deflationary. However, not all coins, such as Dogecoin, are scarce.It has no supply limit.
Coins differ depending on how they are made, their worth, and the role they serve. Here are some examples of different coin types:
Native Coins: These are coins that run on their own blockchain and act as the network’s primary currency. Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), and Litecoin (LTC) are a few examples.
Forked Coins: These are coins that are created by breaking or branching off from an existing blockchain. Bitcoin Cash (BCH), Bitcoin SV (BSV), and Ethereum Classic (ETC) are a few examples.
Wrapped Coins: Coins that represent another asset on another blockchain. They provide users with cross-chain functionality and liquidity. Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC) and Wrapped Ether (WETH) are two examples.
Stablecoins are coins whose value is tied to the worth of another coin.fiat currency or gold are examples of assets. They intend to promote price stability while reducing volatility. Tether (USDT) and USD Coin (USDC) are a couple of instances.
What Exactly Is a Token?
Tokens are built on top of an existing blockchain and rely on it to function. A token can represent a variety of things, including utility, governance rights, ownership shares, and so on.
Tokens are typically “pre-mined,” which means that developers create new tokens and distribute them to users using a smart contract. Tokens have the following properties and benefits:
Tokens are required to use the decentralized applications (dApps) for which they are designed. Tokens can be used by users to pay fees, execute actions, or obtain advantages.
Tokens can give consumers a say in the blockchain or dApp’s decision-making process. Tokens can be used to vote on proposals, modifications, and upgrades.
Tokens can facilitate cross-chain communication and compatibility. Tokens, unlike currencies, can
be supported by several blockchains.
Tokens function as digital currency for the protocol that provides them. They can provide users with access, rights, or prizes.
Tokens are classified according to their function, value proposition, use cases, and so on. Token kinds include the following:
Tokens that provide access to a service or function on the blockchain or dApp are known as utility tokens. Uniswap (UNI) and Chainlink (LINK) are two examples.
Governance Tokens: These tokens allow users to participate in the governance of the blockchain or dApp. Maker (MKR), Compound (COMP), Aave (AAVE), and most other tokens are examples.
Security tokens are tokens that represent a portion of ownership or a claim to an asset or income stream. They are subject to securities regulations and must comply with them. Polymath (POLY) is one example.
Tokens that are not fungible(NFTs): These are digital goods that are unique and indivisible, such as art and collectibles. They are not interchangeable, and their values differ. CryptoPunks and Bored Apes are two examples.
The Difference Between Coin and Token
Let’s look at how coins and tokens differ. Here is a feature-by-feature comparison between coins and tokens:
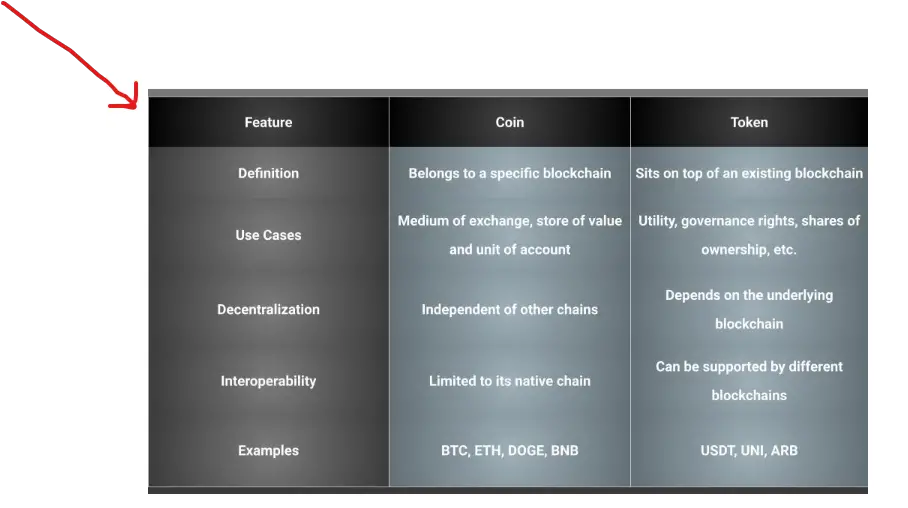
Tokens are more suited for specific uses and value generation, whereas coins are better suited for broad transactions and value preservation. This does not, however, imply that coins and tokens are mutually exclusive or incompatible. They can, in fact, collaborate and complement each other in the crypto ecosystem. As an example:
Users can use coins to purchase tokens or tokens to pay for coin network fees.
Users can access cross-chain functionality and liquidity by wrapping coins into tokens or unwrapping tokens into coins.
Users can earn prizes or participate in governance by staking currency or tokens.
Users can exchange currencies or tokens using decentralized exchanges (DEXs) or automated market makers (AMMs).
Coins and Tokens in Use
Let’s have a look at some of the most popular crypto coins and tokens.
Bitcoin (BTC) is the most popular cryptocurrency.
The first cryptocurrency, and thus the first coin, was Bitcoin. It has grown in popularity as the most secure and decentralized network, with thousands of nodes and miners worldwide.
ETH (Ethereum):
Eth is the Ethereum blockchain’s coin. It functions similarly to Bitcoin as a means of exchange and unit of account. Unlike Bitcoin, Ethereum supports smart contracts and the creation of decentralized apps (DApps).
BNB (Binance Coin):
Binance Coin can be used to pay for discounted trading costs, participate in token sales, and gain access to the Binance ecosystem’s numerous services and functionalities. It also has a finite supply that is burned on a regular basis, resulting in a deflationary impact that enhances its value over time.
DOGE (Dogecoin):
Doge is based on the image of a Shiba Inu dog and has a devoted fan base. It is frequently used on social networking sites for tipping, donating, or expressing support. It is also well-known for having Elon Musk as its unofficial champion and most prominent backer.
Popular Cryptocurrency Tokens
USDT (USDT):
Tether is the most important stablecoin, which means its value is tied to the value of the dollar. Its goal is to offer price stability and lower volatility in the cryptocurrency market. It is frequently used as a means of exchange or a store of value among various cryptocurrencies or platforms.
UNI (Universal Switching):
The Uniswap protocol’s governance token is UNI. Uniswap is a decentralized exchange that allows tokens to be swapped between EVM-compatible blockchains.
Arbitration (ARB):
Arbitrum’s governance token is ARB, which is a layer-two blockchain for Ethereum. Arbitrum was founded by the Arbitrum Foundation and launched with one of the largest airdrops in cryptocurrency history.